Ex.No: Date:
STUDY OF BABCOCK-WILCOX BOILER
Aim: To study
Babcock-Wilcox boiler.
Theory: Evaporating the water at appropriate temperatures and pressures in
boilers does the generation of steam. A boiler
is defined as a set of units, combined together consisting of an apparatus for
producing and recovering heat by igniting certain fuel, together with
arrangement for transferring heat so as to make it available to water, which
could be heated and vaporized to steam form. One of the important types of
boilers is Babcock-Wilcox boiler.
Observation: In thermal powerhouses, Babcock and Wilcox boilers do generation of
steam in large quantities.
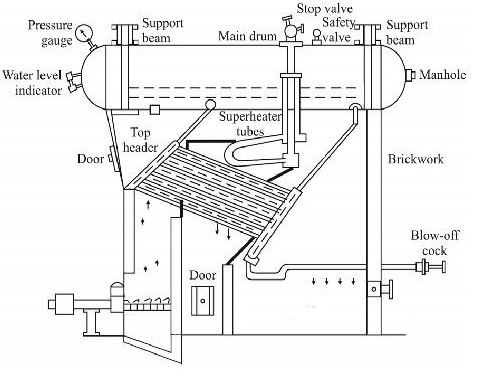
The boiler consists essentially of three parts.
1.
A number of inclined water tubes: They
extend all over the furnace. Water circulates through them and is
heated.
2.
A horizontal stream and water drum: Here
steam separate from the water which is kept
circulating through the tubes and drum.
3.
Combustion chambers: The whole of space where water
tubes are laid is divided into three separate chambers,
connected to each other so that hot gases pass from one to the other and give
out heat in each chamber gradually. Thus the first chamber is the hottest and
the last one is at the lowest temperature. All of these constituents have been
shown as in fig.
The Water tubes 76.2 to 109 mm in
diameter are connected with each other and with the drum by vertical passages
at each end called headers. Tubes are inclined in such a way that they slope
down towards the back. The rear header is called the down-take header and the
front header is called the uptake header has been represented in the fig as DC
and VH respectively.
Whole of the assembly of tubes is
hung along with the drum in a room made of masonry work, lined with fire
bricks. This room is divided into three compartments A, B, and C as shown in
fig, so that first of all, the hot gases rise in A and go down in B, again
rises up in C, and then the led to the chimney through the smoke chamber C. A
mud collector M is attached to the rear and lowest point of the boiler into
which the sediment i.e. suspended impurities of water are collected due to
gravity, during its passage through the down take header. Below the front
uptake header is situated the grate of the furnace, either automatically or
manually fired depending upon the size of the boiler. The direction of hot
gases is maintained upwards by the baffles L.
In the steam and water drum the
steam is separated from the water and the remaining water travels to the back
end of the drum and descends through the down take header where it is subjected
to the action of fire of which the temperature goes on increasing towards the
uptake header. Then it enters the drum where the separation occurs and similar
process continuous further.
For the
purpose of super heating the stream addition sets of tubes of U-shape fixed
horizontally, are fitted in the chamber between the water tubes and the drum.
The steam passes from the steam face of the drum downwards into the super
heater entering at its upper part, and spreads towards the bottom .Finally the
steam enters the water box W, at the bottom in a super heated condition from
where it is taken out through the outlet pipes.
The boiler is fitted with the
usual mountings like main stop valve M, safety valve S, and feed valve F, and
pressure gauge P. Main stop valve is used to regulate flow of steam from the
boiler, to steam pipe or from one steam one steam pipe to other.
The function of safety valve is
used to safe guard the boiler from the hazard of pressures higher than the
design value. They automatically discharge steam from the boiler if inside
pressure exceeds design-specified limit. Feed check valve is used to control
the supply of water to the boiler and to prevent the escaping of water from
boiler due to high pressure inside.
Pressure gauge is an instrument, which record the inside pressure of the
boiler. When steam is raised from a cold boiler, an arrangement is provided for
flooding the super heater. By this arrangement the super
heater is filled with the water up to the level. Any steam is formed while the
super heater is flooded is delivered to the drum ultimately when it is raised
to the working pressure. Now the water is drained off from the super heater
through the cock provided for this purpose, and then steam is let in for super
heating purposes.
Pre
Lab Questions:
1.
What
is the function of boiler?
2.
What
are the different types of boilers?
3.
Explain
the principle of fire tube and water tube boilers?
4.
What
is meant by evaporation?
5.
Differentiate
water tube and fire tube boilers?
Post Lab Questions:
1.
Explain the working principles of various boilers?
2. Advantages of high pressure
boilers?
3.
Explain
the term enthalpy.
4.
Explain
the principles of fluidized bed combustion and pulverized fuel combustion?
5.
What
is the function of superheater, an economizer and an air pre heater?
Conclusion:
|
PO Attainment: |
|
|
Composed By:
R.Satheesh, M.E.,
Asso.Prof.,